Windows Task Manager is used to view details about processes running on computer. Since it can be used to terminate programs that are misbehaving or are viruses disguised in the form of harmless programs, most spyware and viruses disable it to prevent themselves from being closed through it. Some administrators also disable Task Manager to prevent users from closing important security programs like anti-viruses and anti-malwares.
In such situations, running the Task Manager will give the "Task Manager has been disabled by Administrator" error. However, there are some techniques can use to re-enable task manager and close those harmful programs manually. This article contains few such simple techniques to re-enabling Task Manager in a computer running Windows.
⬛ Enable Task Manager using the Registry Editor [Solved]
- Click on Start. Go to Run. (Alternatively, use Windows key+R keyboard shortcut.)
- Type regedit and press Enter. Registry Editor will start. If Registry Editor is also disabled, you will first need to enable registry editing.
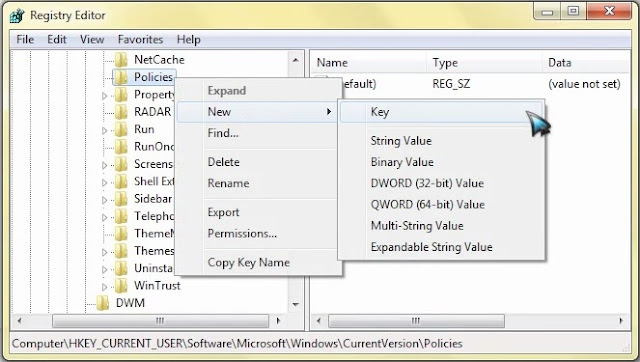
- Through the left-hand navigation pane, navigate to
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\ Windows\ Current Version\Policies\System
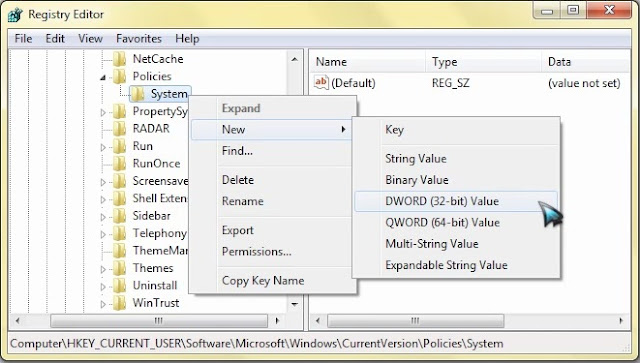
If the System key is not there, you will need to create it. - In the work area, locate "DisableTaskMgr". If this value is not there, you will need to create a new DWORD value called DisableTaskMgr. Double click on it. A window will pop up.
- Enter its value data as 0 and press OK.
- Close Registry Editor.
- Task Manager would immediately be accessible. If it is not, restart the computer.
 |
| Create System Key |
 |
| Create DWORD |
 |
| Windows Task Manager in Windows 7 |
⬛ Enabling Task Manager by creating a Registry(.reg) file
If unfamiliar with manually editing the Registry, just create a Registry file which will automatically modify the Registry Key to re-enable Task Manager.
- Open Notepad.
- Copy the code given below and paste it .
- Save the file as *.reg or Enable Task Manager.reg
- Open this file by double-clicking on it.
- Registry Editor will ask you for confirmation. In the confirmation Window, click Yes.
- Task Manager would immediately be accessible. If it is not, restart computer.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System] “DisableTaskMgr” =dword:00000000
⬛ Enable Task Manager using the Group Policy Editor
- Click on Start. Go to Run. (Alternatively, use Windows key+R keyboard shortcut).
- Type gpedit.msc and press Enter. Group Policy Editor Window will show up.
- Navigate to User Configuration>Administrative Templates>System>Ctrl+Alt+Del Options.
- In the work area, double click on "Remove Task Manager".
- In the popup window, encircle Disabled or Not Configured and click on OK.
- Normally, Task Manager will be immediately accessible. If it is not, restart PC.
Group Policy Editor is not available on home editions of Windows.
⬛ Enable Task Manager by Running a CMD Command
- Open Notepad.
- Copy the code given below and paste it.
- Save the File as TaskManager.bat
- Run this file as Administrator if you use Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7 or Windows Vista. In Windows XP, simply open the file. CMD will flash for a second and then disappear. This indicates successful execution.
- After running the batch file, you will be able to again use Task Manager. If Task Manager is still not available, restart computer.
REG add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Syste /v DisableTaskMgr /t REG_DWORD /d /0 /f
The techniques mentioned in this article work on Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows XP and Windows Vista.













